Blog
What Is NTRIP and How Does It Work?

Network Transport of RTCM via internet Protocol (NTRIP) is a widely adopted GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) technology which improves the delivery of GNSS corrections. NTRIP facilitates the seamless delivery of real-time correction data over the internet. This protocol underpins the delivery of centimeter-level accuracy, critical for industries like automotive, GIS, outdoor robots, and logistics.
Executive Summary
What is NTRIP?
- Network Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) is a widely used GNSS technology for delivering real-time corrections over the internet.
Why NTRIP Matters
- Precision: Helps improve GNSS accuracy from meters to centimeters.
- Convenience: Eliminates line-of-sight requirements and maintenance of base stations.
- Scalability: Supports multiple users and devices simultaneously.
How NTRIP Works
- GNSS base stations collect raw satellite data.
- Corrections are computed at the base station (traditional RTK) or in the cloud (e.g., Skylark).
- Corrections are streamed via an NTRIP caster to rovers using the internet.
- Rovers apply corrections for precise positioning.
Advantages of NTRIP
- Global Coverage: Internet-based delivery works anywhere with connectivity.
- Reduced Interference: Internet transmission avoids common issues with radio signals.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces hardware and maintenance expenses.
Getting Started with NTRIP
- Users need credentials, a compatible GNSS receiver, and an NTRIP client.
Swift Navigation’s Skylark® Precise Positioning Service exemplifies how NTRIP is harnessed to provide instantaneous, highly accurate positioning data – elevating GNSS capabilities to meet modern precision demands.
The Role of NTRIP in GNSS Corrections
NTRIP bridges the gap between GNSS base stations and receivers (often called a rover) by enabling the transfer of correction data. It acts as a data stream, delivering Differential GNSS (DGNSS) and Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) correction signals which are critical for achieving sub-meter to centimeter-level accuracy, making the protocol indispensable for precise positioning.
RTK corrections enhance GNSS data to provide exceptional accuracy. Standard GNSS systems, like GPS, offer location data that is accurate within meters. However, errors introduced by atmospheric interference, satellite orbit inconsistencies, and timing issues can degrade this accuracy. Read our GNSS primer to learn more about the various forms of GNSS corrections.
Here’s how NTRIP works:
1. Raw GNSS Data Collection: Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS), which are strategically placed and have precise known coordinates, observe and collect raw signals from GNSS constellations like GPS, Galileo, and BeiDou.
2. Correction Computation: In Traditional RTK, local base stations use these observations to compute corrections. In the case of a cloud based system, such as Skylark, stations do not compute corrections themselves; they transmit raw observations to the cloud which performs the computation.
3. NTRIP Transmission: A central server called NTRIP caster streams the corrections from base stations to the receiver through the internet. This ensures that correction data is delivered quickly and reliably, enabling real-time, high-accuracy geolocation.
4. Receiver Position Correction: The rover uses the data to correct its position.
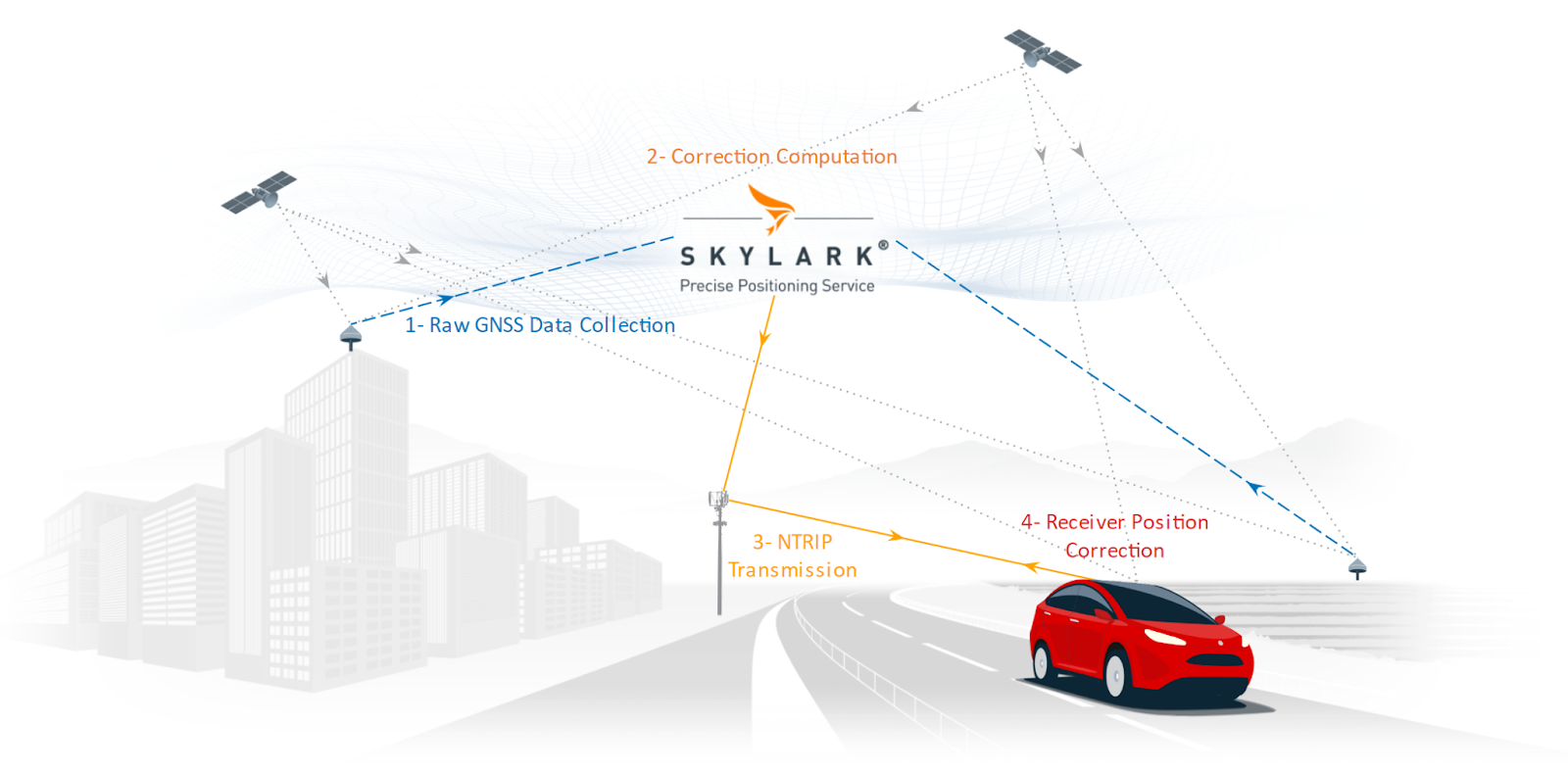
By eliminating the need to manage remote connections to each base station, NTRIP offers a cost-effective and convenient solution for delivering real-time GNSS correction data. Companies looking to implement the highest level of precision in their location-based systems should carefully evaluate their NTRIP service provider to ensure the best possible results.
What are the Advantages of NTRIP over Traditional Systems?
NTRIP provides several advantages over traditional correction delivery methods, such as:
Extended Coverage: Unlike radio systems that are constrained by line-of-sight limitations, NTRIP can deliver corrections globally, as long as an internet connection is available.
Reduced Interference: Internet-based communication is far less susceptible to signal interference compared to radio frequencies.
Cost-Effectiveness: By eliminating the need for companies to own and deploy their own specialized hardware, NTRIP reduces setup and maintenance costs for users.
Scalability: NTRIP systems can support multiple users simultaneously, enabling broader adoption across industries.
These benefits make NTRIP a reliable and versatile choice for delivering high-precision GNSS corrections.
What are the Challenges and Considerations When Using NTRIP?
While NTRIP offers numerous advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
Dependence on Internet Connectivity: NTRIP requires a stable internet connection, which may be a limitation in remote areas with poor network coverage.
Hardware Compatibility: NTRIP requires compatible GNSS receivers and software that can act as an NTRIP client. Not all devices support the required RTCM formats or mount point configurations, potentially limiting its use.
Subscription Costs: Accessing NTRIP services often requires a subscription, which may not be feasible for all users.
How do I Connect to a NTRIP Service?
The general process to connect to a NTRIP service is as follows:
1. Obtain NTRIP credentials from a service provider or local base station. You will need:
- Username/Password
- A Caster URL, which is of the form http://[host]:[port]/[mountpoint]
2. Next, you will require an NTRIP client, most GNSS receivers will have this. The client can take the form of an app if the receiver has bluetooth, or a utility software which can be accessed via serial or USB
To connect to the Skylark NTRIP server, you’ll need to:
1. Sign up to Skylark and purchase a subscription.
2. In the Skylark Portal, add a device to generate a set of NTRIP credentials.
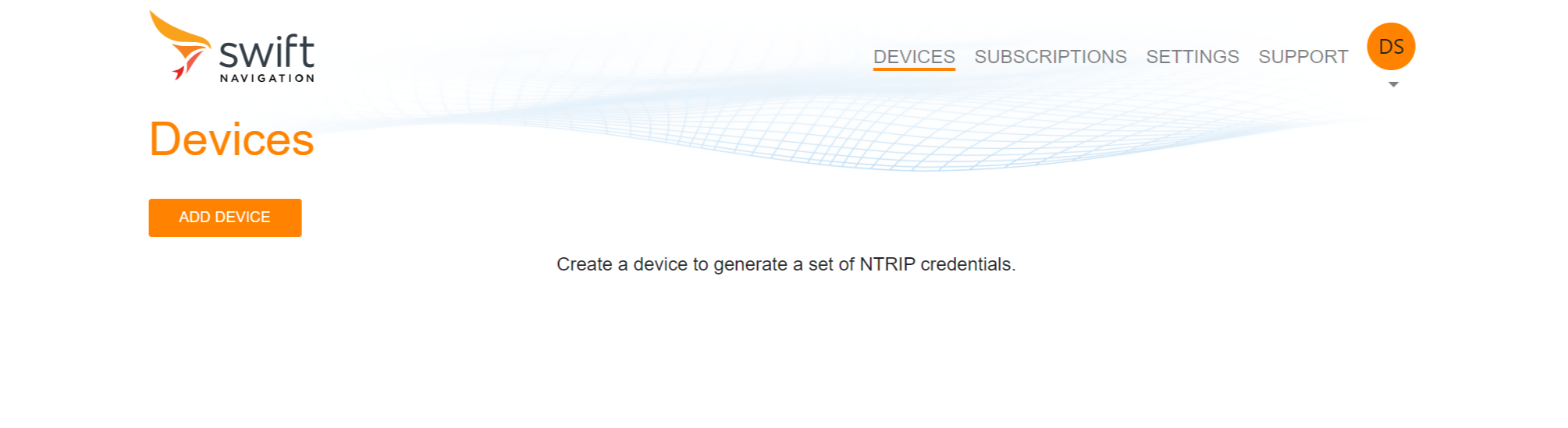
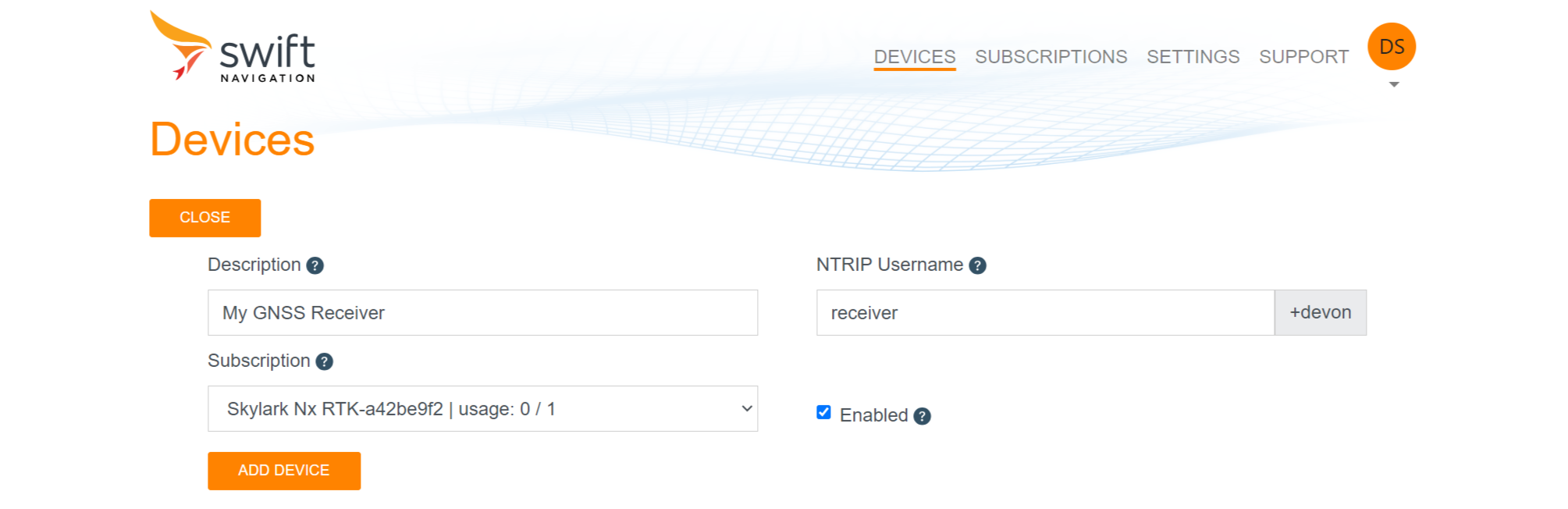
3. Choose your NTRIP username, e.g. 'receiver'.
4. Click ‘View’ to see your NTRIP credentials.
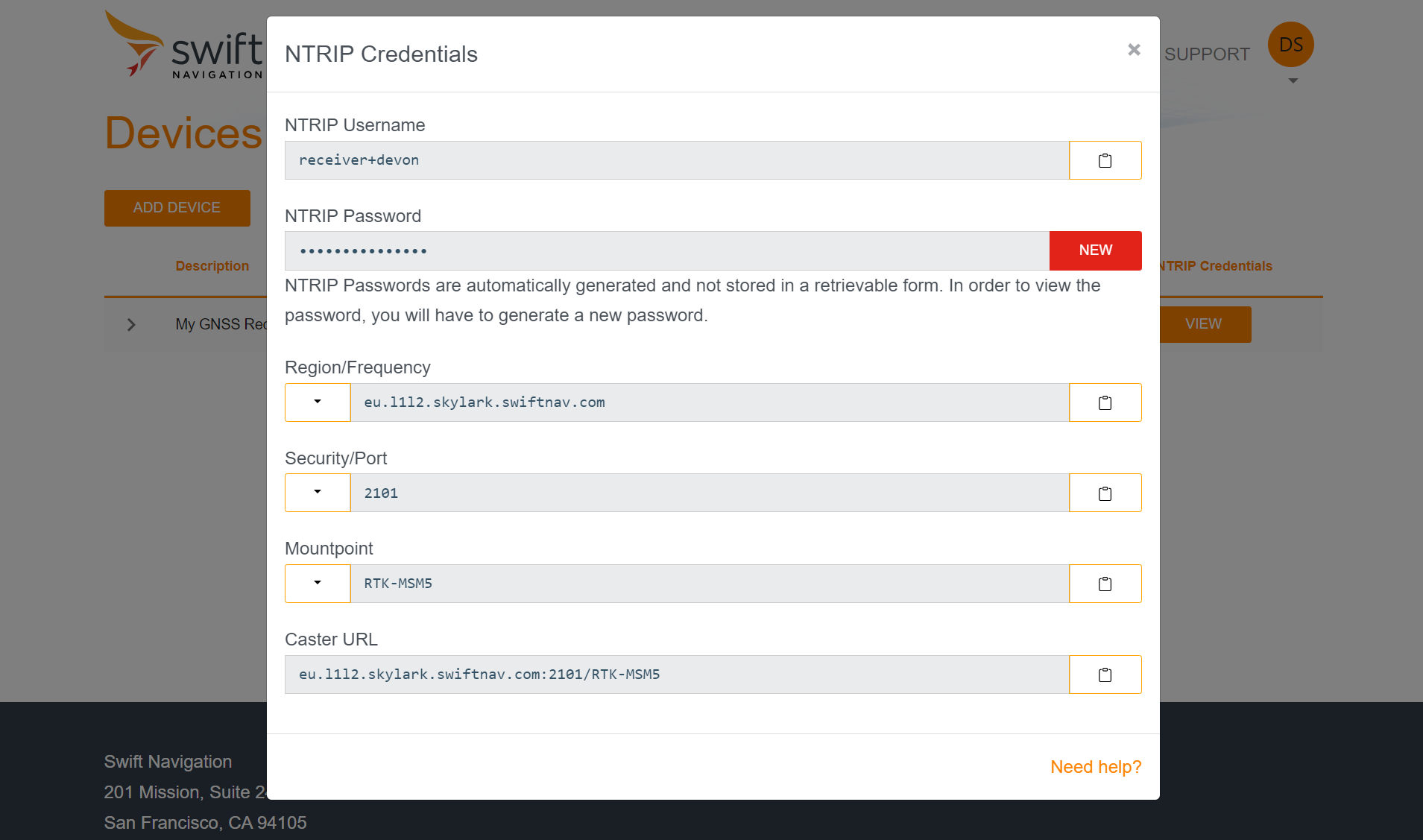
5. Choose the appropriate region (North America, Europe, or Asia Pacific), frequency bands supported by your receiver (L1/L2 or L1/L5), and mount point (RTK-MSM5) in order to get a fully formed Caster URL. Input these credentials and the Caster URL into your GNSS receiver’s NTRIP client interface. Pictured below is the NTRIP configuration in the Bad Elf Flex app.
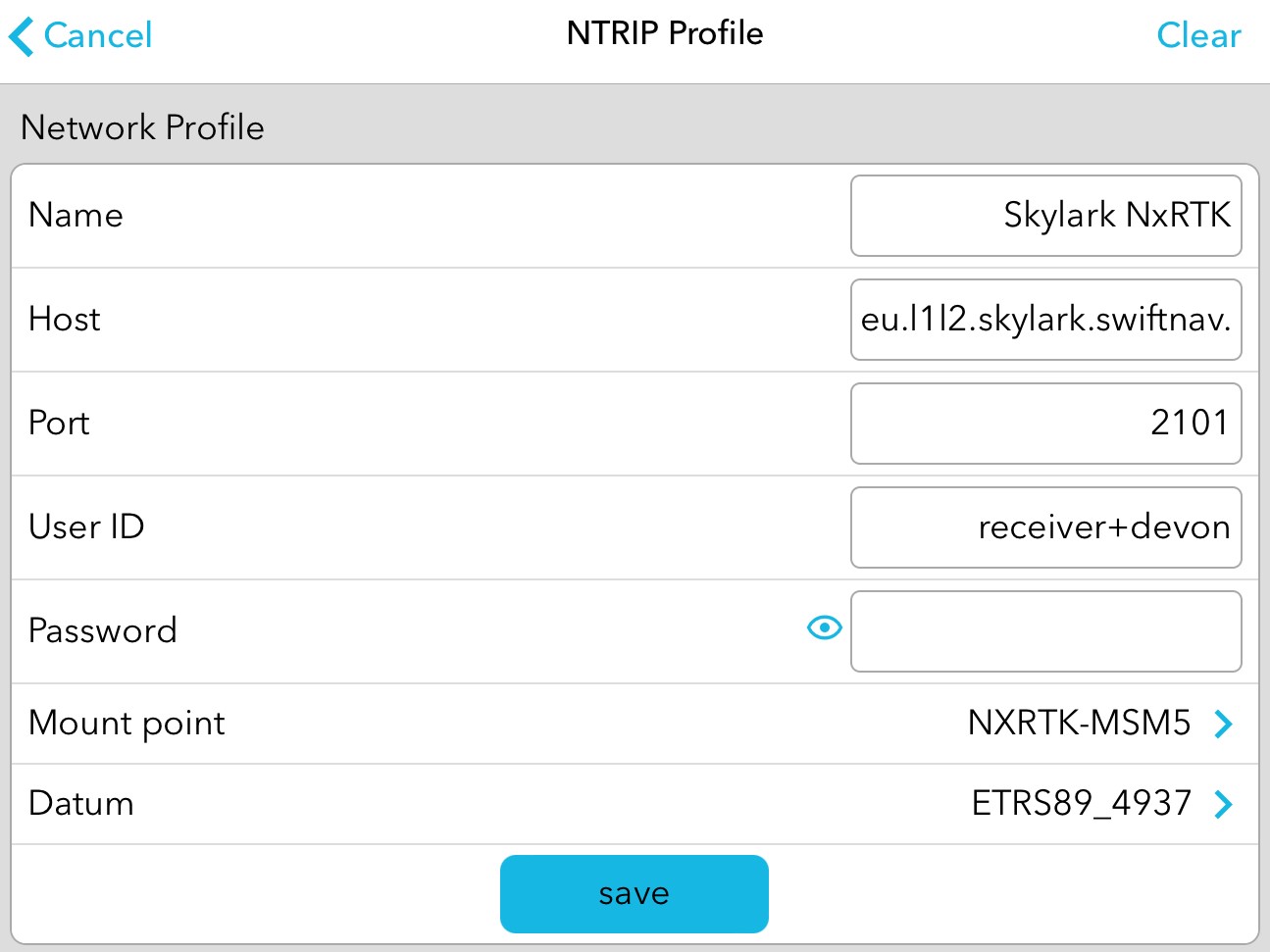
6. Establish the connection and begin receiving GNSS corrections.
NTRIP’s Impact and Emerging Alternatives
Developed under the guidance of the Radio Technical Commission for Maritime Services (RTCM) in 2004 and continuously refined since then, NTRIP has set the benchmark for delivering GNSS corrections. Its reliability and ease of integration make it the preferred protocol for applications demanding highly accurate real-time positioning.
As technology evolves, alternatives like MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) are being explored for certain use cases. These lightweight protocols offer flexibility for real-time data transmission in emerging applications, although they are yet to match NTRIP’s widespread adoption in precision positioning.
NTRIP continues to revolutionize geolocation by providing a reliable, internet-based solution for GNSS corrections. Whether you’re navigating agricultural fields, managing construction sites, or enabling autonomous vehicles, understanding and implementing NTRIP can elevate your operations.
To learn more about configuring NTRIP services or explore solutions tailored to your needs, contact us or sign up for Skylark today.
Read our articles on how to set up the Bad Elf Flex Mini and Emlid Reach RX with RTK corrections for a more detailed overview on connecting your hardware to a NTRIP client.

