White Paper
Skylark Cloud Corrections Cross-Country Drive Test and Dataset
Advancements in technology for connected and autonomous vehicles are rapidly evolving, enabling the automotive industry to enhance mobility and optimize logistics for commercial fleets. The next generation of vehicles will offer immersive navigation, real-time crowdsourced maps, communication with other vehicles and infrastructure, and higher levels of autonomy.
To support these applications, vehicles are equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, including radar, cameras, LiDAR, inertial sensors, and GNSS. While early advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) relied heavily on perception-based sensors and relative positioning, the industry's shift towards full autonomy necessitates the critical absolute positioning provided by GNSS. High accuracy and availability in precise positioning are now essential for safe and reliable assisted and autonomous operations.
Swift’s Cross-Country Drive Test
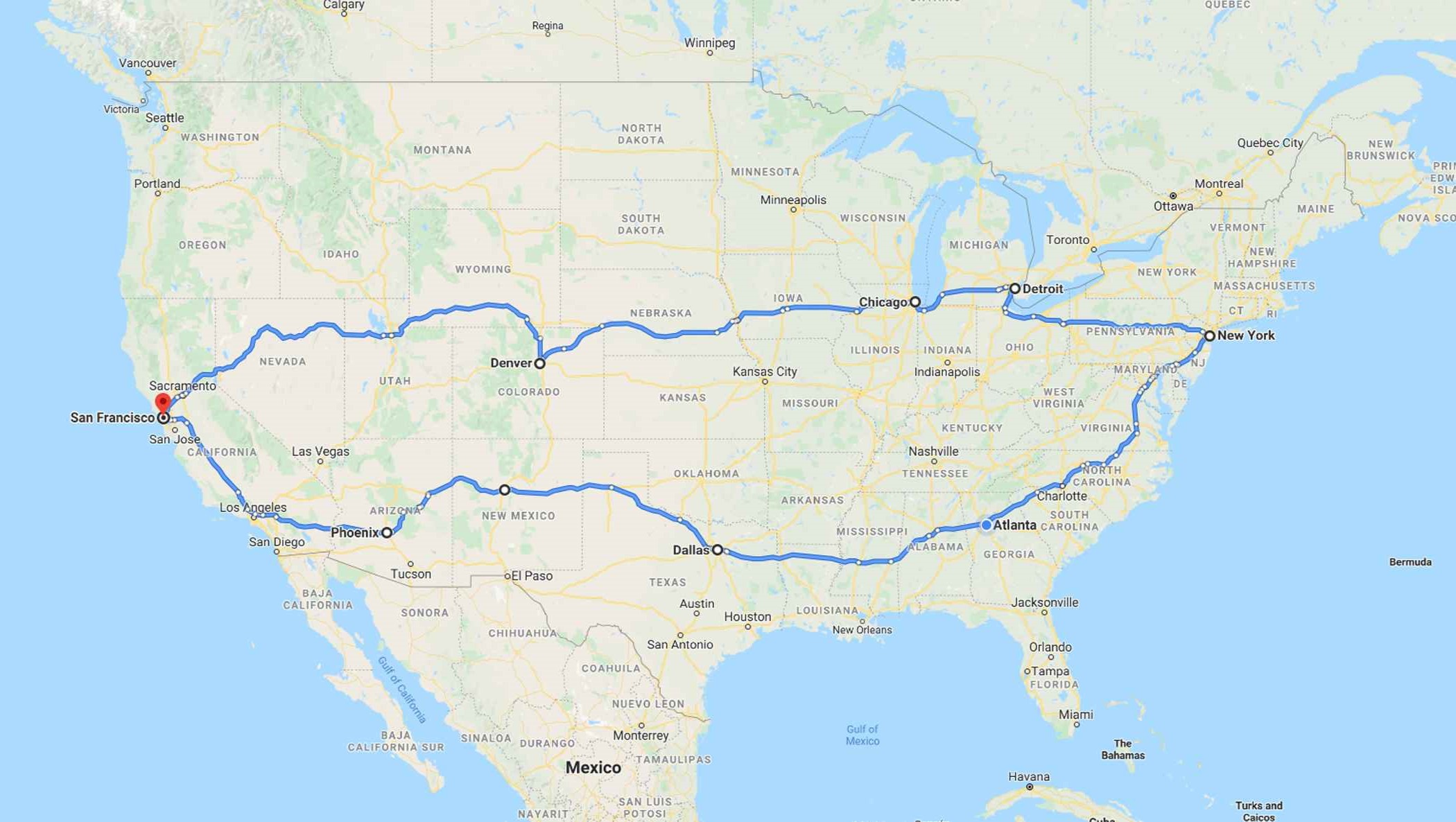
Swift Navigation successfully completed a drive test across the United States, totalling 6,614 miles and covering 26 states. The goal of Swift’s cross-continental drive from San Francisco to New York, and back, was to measure the performance of Skylark, Swift’s cloud-based GNSS corrections service, and to demonstrate true nationwide GNSS coverage at the accuracy levels required by autonomous vehicle applications. This dataset encapsulates the background, set-up, results and data from this drive test.
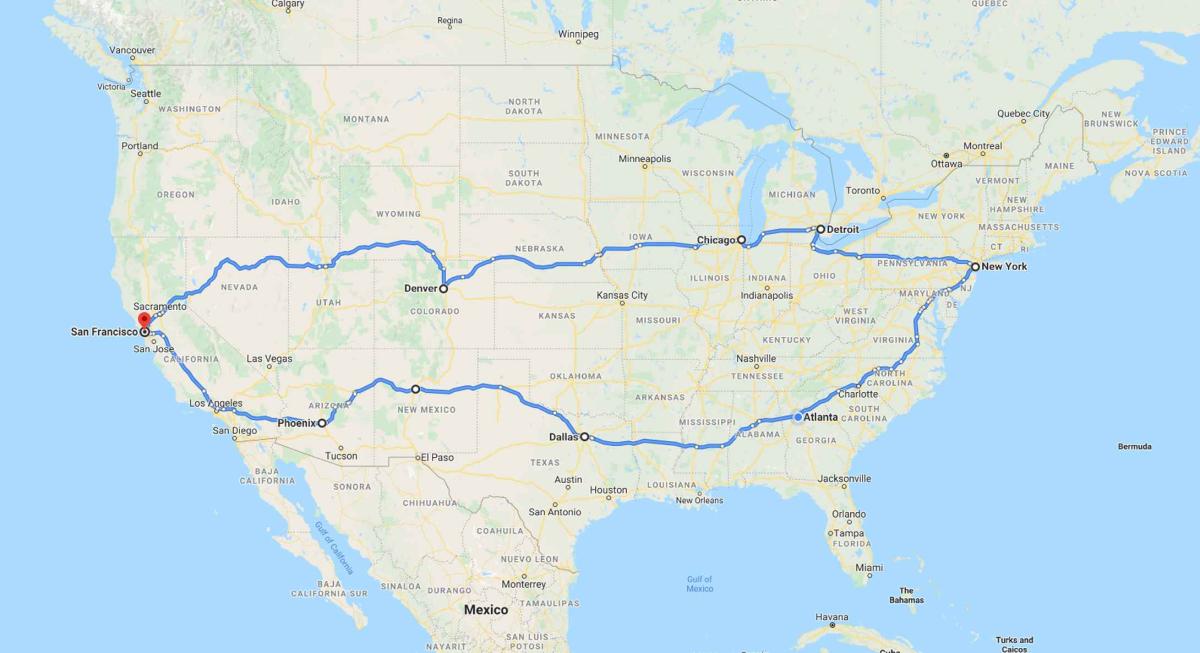
The drive test took a Swift test vehicle through a wide variety of environments as it traversed the United States. From snow in the Sierras of California, to the streets of some of the world’s most bustling metropolises. Under all conditions, Swift’s positioning solution demonstrated its ability to consistently deliver lane-level accuracy. Read the full findings of our drive test and accompanying dataset here.
